[Java] Stack (By ArrayDeque) 따라 구현해보기

ArrayDeque 클래스 특징
① 자바 1.6 추가
② 내부적으로 가변길이 배열(Resizable-array)로 데이터 관리, 용량 제한 없음
③ Thread-safe 하지 않음
④ Null element 금지
⑤ Stack 으로 사용할시 Stack 클래스보다 빠르고, Queue로 사용할 시 LinkedList 클래스보다 빠르다
This class is likely to be faster than Stack when used as a stack, and faster than LinkedList when used as a queue. - 공식 doc
참고. Stack 클래스 단점
자바 1.0에 추가되었고, Vector 클래스를 상속받고 있다 -- LIFO (Last In First Out)
- 멀티 스레드 환경에서 Thread-safe하나, 단일 스레드 환경에서 불필요한 오버헤드가 발생할 수 있다
- 초기 용량 설정할 수 없다
- Vector클래스에서 상속받는 메소드 통해 중간에 element 삭제, 삽입 가능한데, 이는 스택의 데이터 구조(LIFO)가 깨질 위험성을 가지고 있다 (=데이터 정합성/불변성 깨질 수 있다)
public class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> {
public Stack() {}
public E push(E item) { // .. }
public synchronized E pop() { // .. }
public synchronized E peek() { // .. }
public boolean empty() { // .. }
public synchronized int search(Object o) { // .. }
}
Stack 직접 구현해보기
- 기본 용량은 16이고, 데이터 추가시 특정 경우에 배열 크기를 가변하게 된다
- Stack을 구현하는데 필요한 메소드는 아래와 같았다 (간단하게 하기 위해 배열 사이즈 증가 로직은 생략)
public class MyArrayDeque<E> {
Object[] elements;
int head;
int tail;
public MyArrayDeque() {
this.elements = new Object[16]; // default capacity
}
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
public void addFirst(E e) {
//..
}
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
public E removeFirst() {
E e = pollFirst();
if(e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return e;
}
public E pollFirst() {
return null;
}
static final <E> E elementAt(Object[] es, int i) {
return (E) es[i];
}
static final int inc(int i, int modulus) {
if(++i >= modulus) i = 0;
return i;
}
static final int dec(int i, int modulus) {
if(--i < 0) i = modulus - 1;
return i;
}
}
push(E e) - 데이터 추가
- head 포인터가 감소되고, 해당 인덱스에 element 저장됨
- 이때 head 와 tail 위치가 같아진 경우 배열의 사이즈 증가시키고, 데이터를 복사시킨다


구현 메소드는 아래와 같다
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
public void addFirst(E e) {
if(e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
final Object[] es = elements;
es[head = dec(head, elements.length)] = e;
// head == tail 인 경우 배열의 크기를 증가시키고, 데이터를 복사한다 (생략)
}
참고. grow(..) 메소드
oldCapacity 용량이 64보다 작으면 +2만큼 증가, 그 이상인 경우 oldCapacity의 절반만큼 증가시킨다
private void grow(int needed) {
// overflow-conscious code
final int oldCapacity = elements.length;
int newCapacity;
// Double capacity if small; else grow by 50%
int jump = (oldCapacity < 64) ? (oldCapacity + 2) : (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (jump < needed
|| (newCapacity = (oldCapacity + jump)) - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = newCapacity(needed, jump);
final Object[] es = elements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, newCapacity);
// Exceptionally, here tail == head needs to be disambiguated
if (tail < head || (tail == head && es[head] != null)) {
// wrap around; slide first leg forward to end of array
int newSpace = newCapacity - oldCapacity;
System.arraycopy(es, head,
es, head + newSpace,
oldCapacity - head);
for (int i = head, to = (head += newSpace); i < to; i++)
es[i] = null;
}
}
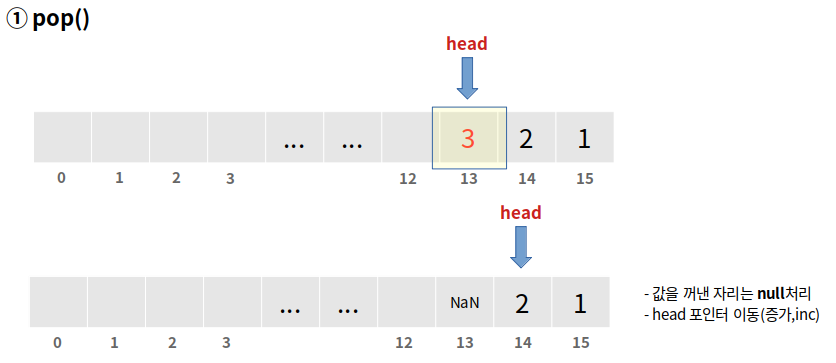
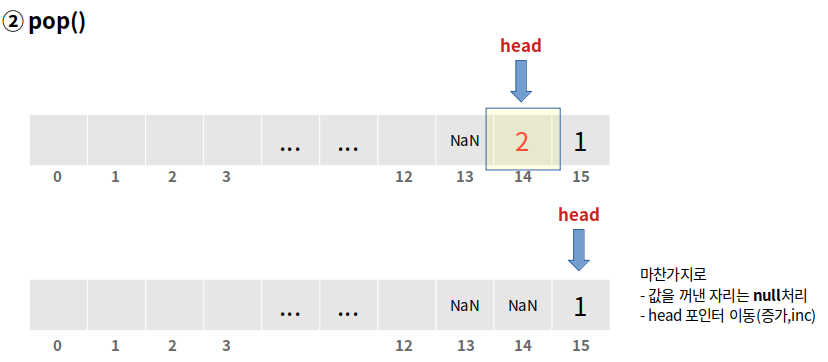
pop() - 데이터 꺼내기
- head 위치에 있는 데이터를 꺼낸다
- 데이터가 null이 아닌 경우 elements[head] = null 처리한다
- 그리고 head를 +1만큼 이동시킨다
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
public E removeFirst() {
E e = pollFirst();
if(e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return e;
}
public E pollFirst() {
final Object[] es = elements;
E e = elementAt(es, head);
if(e != null) {
es[head] = null;
head = inc(head, es.length); // head 증가
}
return e;
}
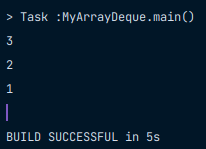
테스트 결과
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayDeque<Integer> stack = new MyArrayDeque<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}