[Next Step] 8장 Ajax를 활용해 새로고침 없이 데이터 갱신하기

실습 프로젝트 저장소
실습의 경우 처음에 fork 받았는데, 깃 허브 잔디가 심어지지 않아 기술 블로그 참고(링크)하여 저장소 설정을 변경하도록 함
jwp-basic
https://github.com/slipp/jwp-basic/tree/step4-qna-getting-started
GitHub - slipp/jwp-basic: 자바 웹 프로그래밍 기본 실습
자바 웹 프로그래밍 기본 실습. Contribute to slipp/jwp-basic development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
8장 AJAX를 활용해 새로고침 없이 데이터 갱신하기
- 이번 장에서는 질문 목록/상세, 답변 목록/생성/삭제 화면 및 기능 구현 후 리팩토링을 수행한다
- 책에는 없는 내용이 많으므로 깃 저장소를 참고하여 필요한 부분은 보충하도록 한다
- 질문/답변 구현은 다루지 않습니다
참고.
arguments 객체 - JavaScript | MDN
arguments 객체는 함수에 전달된 인수에 해당하는 Array 형태의 객체입니다.
developer.mozilla.org
Callback in the replace mathod int JavaScript
Callback in the replace method in JavaScript regexes | Trepachev Dmitry
The replace method as the second parameter can take not only a string, but also a callback function, which will be applied for each match found. Each substring that the regex has found will be replaced by what the function returns for this particular subst
code.mu
PreparedStatementCreator 인터페이스
- Connection 객체를 받아 PreparedStatement 객체를 콜백 인터페이스 활용하여 생성 후 반환하는 인터페이스
- org.springframework.jdbc.core.PreparedStatementCreator 클래스와 동일
public interface PreparedStatementCreator {
PreparedStatement createPreparedStatement(Connection con) throws SQLException;
}
KeyHolder POJO클래스 용도
public class KeyHolder {
private long id;
//getter, setter 생략
}
JdbcTemplate에 update method를 오버로딩 → 신규 데이터 추가 후 기본 키 값을 가져옴 → KeyHolder 통해 id값 전달 → 해당 id값으로 조회
AnswerDao, QuestionDao 테스트 & 클래스 구현
AnswerDaoTest
public class AnswerDaoTest {
@BeforeEach
public void setup() {
ResourceDatabasePopulator populator = new ResourceDatabasePopulator();
populator.addScript(new ClassPathResource("jwp.sql"));
DatabasePopulatorUtils.execute(populator, ConnectionManager.getDataSource());
}
@Test
void insert() {
//given
Date now = new Date();
Answer givenAnswer = new Answer(0, "jinwoo", "내용없음체", now, Long.valueOf(1));
//when
AnswerDao answerDao = new AnswerDao();
Answer result = answerDao.insert(givenAnswer);
//then
assertThat(result).isNotNull();
assertThat(result.getTimeFromCreateDate()).isEqualTo(now.getTime());
assertThat(result).extracting("writer", "contents", "questionId")
.containsExactlyInAnyOrder("jinwoo", "내용없음체", Long.valueOf(1));
}
@DisplayName("answerId 값으로 답변 Answer를 가져온다")
@Test
void findById() {
//given
long answerId = 1L;
//when
AnswerDao answerDao = new AnswerDao();
Answer result = answerDao.findById(answerId);
//then
assertThat(result).isNotNull();
assertThat(result.getAnswerId()).isEqualTo(answerId);
}
@Test
void findAllByQuestionId() {
//given
long questionId = 7L;
//when
AnswerDao answerDao = new AnswerDao();
List<Answer> result = answerDao.findAllByQuestionId(questionId);
//then
assertThat(result).hasSize(2);
assertThat(result).extracting("questionId")
.containsOnly(questionId);
}
@Test
void delete() {
// given
long questionId = 7L;
//when
AnswerDao answerDao = new AnswerDao();
answerDao.delete(questionId);
List<Answer> result = answerDao.findAllByQuestionId(questionId);
assertThat(result).isEmpty();
}
}
QuestionDaoTest
public class QuestionDaoTest {
@BeforeEach
public void setup() {
ResourceDatabasePopulator populator = new ResourceDatabasePopulator();
populator.addScript(new ClassPathResource("jwp.sql"));
DatabasePopulatorUtils.execute(populator, ConnectionManager.getDataSource());
}
@Test
void findAll() {
//given
//when
QuestionDao questionDao = new QuestionDao();
List<Question> result = questionDao.findAll();
//then
assertThat(result).hasSize(8);
}
@Test
void findById() {
//given
long questionId = 1L;
//when
QuestionDao questionDao = new QuestionDao();
Question question = questionDao.findById(questionId);
//then
assertThat(question)
.isNotNull()
.extracting("questionId", "writer", "title")
.containsExactly(questionId, "자바지기", "국내에서 Ruby on Rails와 Play가 활성화되기 힘든 이유는 뭘까?");
}
}
PreparedStatementCreator 인터페이스
public interface PreparedStatementCreator {
PreparedStatement createPreparedStatement(Connection con) throws SQLException;
}
PreparedStatementSetter 인터페이스
public interface PreparedStatementSetter {
void values(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException;
}
RowMapper 인터페이스
public interface RowMapper<T> {
T mapRow(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException;
}
MyJdbcTeamplte 클래스
PreparedStatementCreator 인터페이스 구현체와 KeyHolder POJO 객체를 인자로 받는 update() 메소드가 추가되었다
public class MyJdbcTemplate<T> {
[..]
// AnswerDao에서 PreparedStatementCreator 구현해서 콜백 함수 실행
public void update(PreparedStatementCreator psc, KeyHolder holder) throws DataAccessException {
try (Connection con = ConnectionManager.getConnection()){
PreparedStatement ps = psc.createPreparedStatement(con);
ps.executeUpdate();
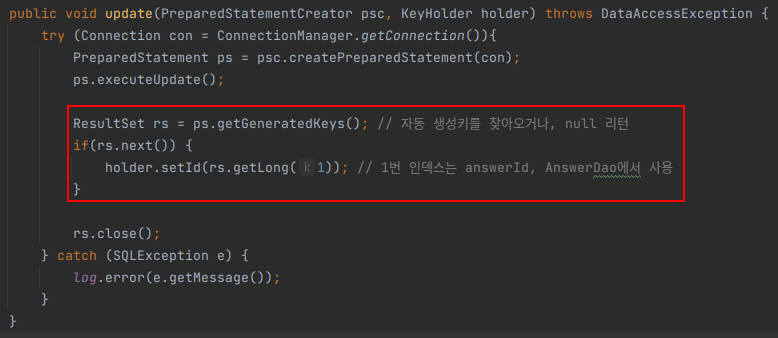
ResultSet rs = ps.getGeneratedKeys(); // 자동 생성키를 찾아오거나, null 리턴
if(rs.next()) {
holder.setId(rs.getLong(1)); // 1번 인덱스는 answerId, AnswerDao에서 사용
}
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.error(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
AnswerDao 클래스
public class AnswerDao {
public Answer insert(Answer answer) {
MyJdbcTemplate<Answer> jdbcTemplate = new MyJdbcTemplate();
String sql = "INSERT INTO ANSWERS (writer, contents, createdDate, questionId) VALUES(?, ?, ?, ?)";
PreparedStatementCreator psc = (con) -> {
PreparedStatement ps = con.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, answer.getWriter());
ps.setString(2, answer.getContents());
ps.setTimestamp(3, new Timestamp(answer.getTimeFromCreateDate()));
ps.setLong(4, answer.getQuestionId());
return ps;
};
KeyHolder keyHolder = new KeyHolder();
jdbcTemplate.update(psc, keyHolder);
return findById(keyHolder.getId());
}
public Answer findById(long answerId) {
MyJdbcTemplate<Answer> jdbcTemplate = new MyJdbcTemplate();
String sql = "SELECT answerId, writer, contents, createdDate, questionId FROM ANSWERS WHERE answerId = ?";
RowMapper<Answer> rowMapper = (rs) -> new Answer(
rs.getLong("answerId"),
rs.getString("writer"),
rs.getString("contents"),
rs.getTimestamp("createdDate"),
rs.getLong("questionId"));
return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, rowMapper, answerId);
}
public List<Answer> findAllByQuestionId(long questionId) {
MyJdbcTemplate<Answer> jdbcTemplate = new MyJdbcTemplate<>();
String sql = "SELECT answerId, writer, contents, createdDate, questionId FROM ANSWERS WHERE questionId = ?";
RowMapper<Answer> rowMapper = (rs) -> new Answer(
rs.getLong("answerId"),
rs.getString("writer"),
rs.getString("contents"),
rs.getTimestamp("createdDate"),
rs.getLong("questionId"));
return jdbcTemplate.query(sql, rowMapper, questionId);
}
public void delete(long answerId) {
MyJdbcTemplate<Answer> jdbcTemplate = new MyJdbcTemplate<>();
String sql = "DELETE FROM ANSWERS WHERE answerId = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, answerId);
}
}
QuestionDao 클래스
public class QuestionDao {
// 전체 목록 (이때 content = null)
public List<Question> findAll() {
MyJdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new MyJdbcTemplate();
String sql = "SELECT questionId, writer, title, createdDate, countOfAnswer " +
"FROM QUESTIONS ORDER BY questionId desc";
RowMapper<Question> rm = (rs) ->
new Question(
rs.getLong("questionId"),
rs.getString("writer"),
rs.getString("title"),
null,
rs.getTimestamp("createdDate"),
rs.getInt("countOfAnswer")
);
return jdbcTemplate.query(sql, rm);
}
// 상세보기
public Question findById(long questionId) {
MyJdbcTemplate<Question> jdbcTemplate = new MyJdbcTemplate();
String sql = "SELECT questionId, writer, title, contents, createdDate, countOfAnswer " +
"FROM QUESTIONS WHERE questionId = ?";
RowMapper<Question> rm = (rs) ->
new Question(
rs.getLong("questionId"),
rs.getString("writer"),
rs.getString("title"),
rs.getString("contents"),
rs.getTimestamp("createdDate"),
rs.getInt("countOfAnswer")
);
return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, rm, questionId);
}
}MVC 프레임워크 요구사항 2단계
p287
질문/답변 게시판 기능을 추가하면서 AJAX 기능을 지원하려고 보니 MVC 프레임워크 구조에 빈틈이 보이기 시작했다.
public class DeleteAnswerController implements Controller {
@Override
public String execute(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws Exception {
[..]
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
resp.setContentType("application/json?charset=UTF-8");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
out.print(mapper.writeValuesAsString(Result.ok()));
return null; //*
}
}위의 코드에서 2가지 문제점이 확인된다
① 불필요하게 null을 리턴하고 있다
② 자바 객체를 JSON으로 변환하고 응답하는 부분에서 중복이 발생한다
Hint (p289~290)
경우의 수가 증가하면서 if/else 절이 계속 발생하는 상황은 앞에서도 경험했다. 앞에서 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 Controller 인터페이스를 추가했듯이 뷰를 추상화한 인터페이스를 추가한다.
public interface View {
void render(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception;
}
① View를 구현하는 JspView와 JsonView를 생성해 각 View 성격에 맞도록 구현한다
② Controller 인터페이스의 반환 값을 String에서 View로 변경한다
③ 각 Controller에서 String 대신 JspView 또는 JsonView 중 하나를 사용하도록 변경한다
④ DispatcherServlet에서 String 대신 View 인터페이스를 사용하도록 수정한다
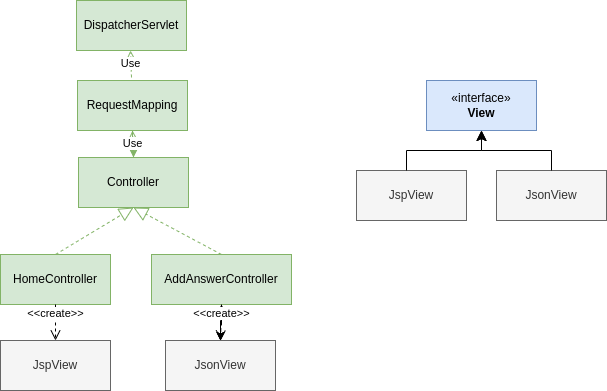
View 인터페이스 추가
public interface View {
void render(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception;
}
JspView와 JsonView 추가
JspView 클래스
public class JspView implements View {
private static final String DEFAULT_REDIRECT_PREFIX = "redirect:";
private String viewName;
public JspView(String viewName) {
if(viewName == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("viewName is null. 이동할 URL을 추가해 주세요");
}
this.viewName = viewName;
}
//redirect, forward 처리 로직이 옮겨지면서 DispatcherServlet 클래스가 간소화 되었다
@Override
public void render(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if(viewName.startsWith(DEFAULT_REDIRECT_PREFIX)) {
response.sendRedirect(viewName.substring(DEFAULT_REDIRECT_PREFIX.length()));
return;
}
RequestDispatcher rd = request.getRequestDispatcher(viewName);
rd.forward(request, response);
}
}
JsonView 클래스
public class JsonView implements View {
public JsonView() {
}
@Override
public void render(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.print(mapper.writeValueAsString(createModel(request)));
}
private Map<String, Object> createModel(HttpServletRequest request) {
Enumeration<String> attributeNames = request.getAttributeNames(); // 이슈*
Map<String, Object> model = new HashMap<>();
while(attributeNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String name = attributeNames.nextElement();
model.put(name, request.getAttribute(name));
}
return model;
}
}
DispatcherServlet 리팩토링
응답 데이터 처리에 대한 책임을 View에 위임
public class DispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
[..]
Controller controller = rm.get(requestUrl);
try {
View view = controller.execute(req, resp);
view.render(req, resp);
} catch (Exception e) {
// ..
}
}
}
HttpServletRequest를 사용하면서 발생하는 하나의 이슈는 JsonView는 HttpServletRequest에 추가되어 있는 모든 데이터를 JSON으로 변경한다. 그런데 HttpServletRequest의 경우 서블릿 필터, 서블릿의 여러 단계를 거치면서 개발자가 모르는 상태에서 값이 추가되는 상황이 발생할 수 있다. 이 경우 개발자가 의도하지 않은 데이터까지 불필요하게 추가되어 JSON 응답으로 클라이언트에게 보내질 수 있다.
HttpServletRequest를 통해 데이터를 전달하지 않고 개발자가 원하는 데이터만 뷰로 전달 할 수 있도록 모델 데이터 대한 추상화 작업을 진행해 본다.
Model 데이터에 대한 추상화 작업을 진행한다.
① Model 데이터를 View와 같이 전달해야 하기 때문에 ModelAndView와 같은 이름의 클래스를 새로 추가한다
② ModelAndView는 View와 모델 데이터를 Map<String, Object> 형태로 관리하도록 구현한다
ModelAndView 추가를 통한 모델 추상화
public class ModelAndView {
private View view;
private Map<String, Object> model = new HashMap<>();
public ModelAndView(View view) {
this.view = view;
}
public ModelAndView addAttribute(String key, Object value) {
model.put(key, value);
return this;
}
public Map<String, Object> getModel() {
return Collections.unmodifiableMap(model);
}
public View getView() {
return view;
}
}
View 인터페이스의 render() 메소드의 인자에 Map<String, Object> model 데이터를 인자로 전달할 수 있도록 변경한다
public interface View {
void render(Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception;
}
View 인터페이스 변경에 따라 JspView와 JsonView 클래스를 다음과 같이 수정한다
JspView 클래스
@Override
public void render(Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if(viewName.startsWith(DEFAULT_REDIRECT_PREFIX)) {
response.sendRedirect(viewName.substring(DEFAULT_REDIRECT_PREFIX.length()));
return;
}
Set<String> keys = model.keySet(); //*
for(String key : keys) {
request.setAttribute(key, model.get(key));
}
RequestDispatcher rd = request.getRequestDispatcher(viewName);
rd.forward(request, response);
}*model에 있는 값만 클라이언트에게 응답하게 된다
JsonView 클래스
public class JsonView implements View {
[..]
@Override
public void render(Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.print(mapper.writeValueAsString(model)); //*
}
}*{key : value} 형태로 JSON 응답 데이터를 보내게 된다
Controller 인터페이스의 반환 값을 View에서 ModelAndView로 수정한다
public interface Controller {
ModelAndView execute(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception;
}
ModelAndView 생성을 좀 더 쉽도록 도와주기 위해 AbstractController를 추가한 후 두 개의 메소드를 제공한다
public abstract class AbstractController implements Controller {
protected ModelAndView jspView(String viewName) {
return new ModelAndView(new JspView(viewName));
}
protected ModelAndView jsonView() {
return new ModelAndView(new JsonView());
}
}
Controller 구현체를 리팩토링한다
JsonView() 사용할 경우
public class AddAnswerController extends AbstractController {
@Override
public ModelAndView execute(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
[..]
return jsonView().addAttribute("data", savedAnswer);
}
}
JspView() 사용할 경우
public class ShowController extends AbstractController {
@Override
public ModelAndView execute(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
[..]
return jspView("/qna/show.jsp")
.addAttribute("question", questionDao.findById(questionId))
.addAttribute("answerList", answerDao.findAllByQuestionId(questionId));
}
}
DispatcherServlet 리팩토링(최종)
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
[..]
Controller controller = rm.get(requestUrl);
try {
ModelAndView modelAndView = controller.execute(req, resp);
View view = modelAndView.getView();
view.render(modelAndView.getModel(), req, resp);
} catch (Exception e) {
//..
}
}좋은 글 (p301)
“시작단계부터 모든 요구사항을 파악해 설계한 후 구현할 수 있다면 정말 좋겠다. 하지만 시작단계에서 모든 요구사항을 파악하는 것은 거의 불가능에 가깝다. 특히 비즈니스 세계에서는 오늘 맞는 답이 내일은 틀린 답이 될 수 있다. 지금과 같이 빠르게 변화하는 세상에서 완벽한 설게란 없다. 그렇기 때문에 애플케이션을 구현하는 시점에 할 수 있는 능력을 끼우는 것이 이 시대를 살아가는 개발자가 갖추어야 할 능력이라 할 수 있겠다. 이 같은 맥락에서 테스트와 리팩토링은 그 무엇보다 중요한 활동이다. 더불어 유연한 객체지향 개발 또한 빠르게 변화하는 세상에 대응할 수 있는 무기가 될 수 있다. 하지만 세상에 정답은 없다. .. (중략) 어쩌면 개발자가 진정 갖추어야 할 가장 중요한 능력은 프로젝트 상황에 맞는 적절한 방법을 찾아 적용하는 능력일 것이다.”