[BOJ 10942] 팰린드롬 ? (Java, DP)

문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/10942
10942번: 팰린드롬?
총 M개의 줄에 걸쳐 홍준이의 질문에 대한 명우의 답을 입력으로 주어진 순서에 따라서 출력한다. 팰린드롬인 경우에는 1, 아닌 경우에는 0을 출력한다.
www.acmicpc.net
문제 풀이
시간복잡도
- 상향식(Bottom-Up) 풀이시 O(N^2) = O(2000^2)
- 하향식(Top-Down) 풀이시 O(N!) = O(2000!) 시간 초과 발생 가능 -> memorization 기법으로 시간내 풀이 가능
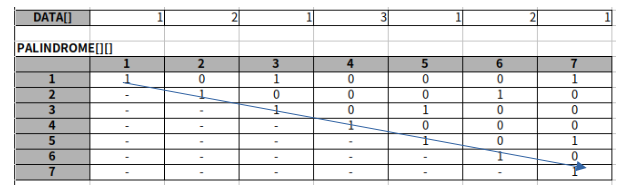
*팰린드롬 (PALINDROME) ?
- 길이가 1일 때 자기 자신도 팰린드롬이다. (1, 2, 3, ...)
- 길이가 2인 경우 두 숫자가 동일할때 팰린드롬이다. (11, 22)
- 길이가 3인 경우 시작과 끝 수가 동일하고, 시작과 끝 사이 범위가 펠린드롬인 경우 팰린드롬이다
예) PALIDROME[1][7] 에서 시작과 끝이 1로 동일하고 사이에 있는 21312 또한 팰린드롬이다.
길이가 3이상일 때
PALIDROME[i][j] = (A[i] == A[j] && PALIDROME[i + 1][j - 1]) ? 1 : 0;
행 단위로 채워지던 DP 문제와 달리 팰린드롬의 경우 사선 방향으로 채워지는 형태를 보인다
제출 코드
(1) Bottom-Up
- 미리 PALINDROME 배열을 구하고, Query에 대한 결과값을 출력
- Query 가 최대 1,000,000인 경우더라도 배열 조회하는 데 O(1) 시간 복잡도 소요
- 따라서 전처리로 PALINDROME 배열 구하는데 소요되는 O(N^2)이 최종 시간 복잡도
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
static InputProcessor inputProcessor = new InputProcessor();
static String NEW_LINE = System.lineSeparator();
static int N, M;
static int[] DATA;
static boolean[][] PALINDROME;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
input();
preprocess();
pro();
M = inputProcessor.nextInt();
for(int i = 1; i <= M; i++) {
int s = inputProcessor.nextInt();
int e = inputProcessor.nextInt();
sb.append(PALINDROME[s][e] ? 1 : 0).append(NEW_LINE);
}
output();
}
private static void preprocess() {
PALINDROME = new boolean[N + 1][N + 1];
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
PALINDROME[i][i] = true;
}
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
if(DATA[i] == DATA[i + 1]) {
PALINDROME[i][i + 1] = true;
}
}
}
private static void input() {
N = inputProcessor.nextInt();
DATA = new int[N + 1];
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
DATA[i] = inputProcessor.nextInt();
}
}
private static void pro() {
for(int len = 3; len <= N; len++) {
for(int i = 1; i <= N - len + 1; i++) {
int j = i + len - 1;
if(DATA[i] == DATA[j] && PALINDROME[i + 1][j - 1]) {
PALINDROME[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
}
private static void output() throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
bw.write(sb.toString());
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}
private static class InputProcessor {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public InputProcessor() {
this.br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public String next() {
while(st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public String nextLine() {
String input = "";
try {
input = br.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return input;
}
public int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
}
}
(2) Top-Down
- 동일하게 길이가 1과 2일때 초기화
- 나머지의 경우 방문하지 않았다는 의미에서 -1 초기화 (메모리제이션 기법에 사용)
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
static InputProcessor inputProcessor = new InputProcessor();
static String NEW_LINE = System.lineSeparator();
static int N, M;
static int[] DATA;
static int[][] PALINDROME;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
input();
preprocess();
M = inputProcessor.nextInt();
for(int i = 1; i <= M; i++) {
int s = inputProcessor.nextInt();
int e = inputProcessor.nextInt();
sb.append(topDown(s, e)).append(NEW_LINE);
}
output();
}
private static int topDown(int s, int e) {
if(s == e) return 1;
if(PALINDROME[s][e] != -1) return PALINDROME[s][e];
return PALINDROME[s][e] = (DATA[s] == DATA[e] && topDown(s + 1, e - 1) == 1) ? 1 : 0;
}
private static void preprocess() {
PALINDROME = new int[N + 1][N + 1];
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
Arrays.fill(PALINDROME[i], 1, N + 1, -1);
PALINDROME[i][i] = 1;
}
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
if(DATA[i] == DATA[i + 1]) PALINDROME[i][i + 1] = 1;
else PALINDROME[i][i + 1] = 0;
}
}
private static void input() {
N = inputProcessor.nextInt();
DATA = new int[N + 1];
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
DATA[i] = inputProcessor.nextInt();
}
}
private static void output() throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
bw.write(sb.toString());
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}
private static class InputProcessor {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public InputProcessor() {
this.br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public String next() {
while(st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public String nextLine() {
String input = "";
try {
input = br.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return input;
}
public int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
}
}